At Coffee-Bike, your mobile coffee bar for events, everything revolves around a passion for coffee – from the plant to the perfect coffee speciality. In this blog post, we share our knowledge, tips and exciting information about coffee cultivation. Because anyone who works with high-quality beans every day knows how much craftsmanship, patience and dedication goes into every single caffeinated hot drink.
Coffee cultivation: From the coffee plant to the bean to the cup
29.10.2025 | Coffee know-how

Basics – Where and how coffee is grown
Coffee cultivation lays the foundation for what will later end up in your cup. Climate, soil and location determine how the plant grows and what character the beans develop. In the following sections, you will learn where coffee is grown worldwide, what special features the growing regions have and how the origin of the plants influences the taste of the beans.
Introduction to coffee cultivation – the best growing regions worldwide
Coffee is cultivated in over 70 countries, mainly in the most common varieties, Arabica and Robusta. Numerous plantations and fields are found primarily in the so-called ‘coffee belt’ region around the equator. All growing regions give coffee a unique aroma. But what conditions does the coffee plant need to grow?
Climate: Coffee plants thrive best in a consistently warm, tropical climate with sufficient rainfall and some shade.
Altitude: Higher altitudes offer ideal conditions for growing coffee. The slower ripening of the beans results in a more intense and multifaceted aroma profile.
Soil conditions: The soil in which the coffee grows has a significant influence on its subsequent flavour. Whether volcanic soil, loamy earth or sandy subsoil, each leaves its own characteristic notes.
The coffee plant: care and harvesting
The coffee plant, scientifically known as ‘Coffea’, requires a lot of attention and careful care in order to bear healthy fruit. Depending on the growing region, farmers can harvest once or twice a year, with the harvest time being crucial for the quality of the beans.
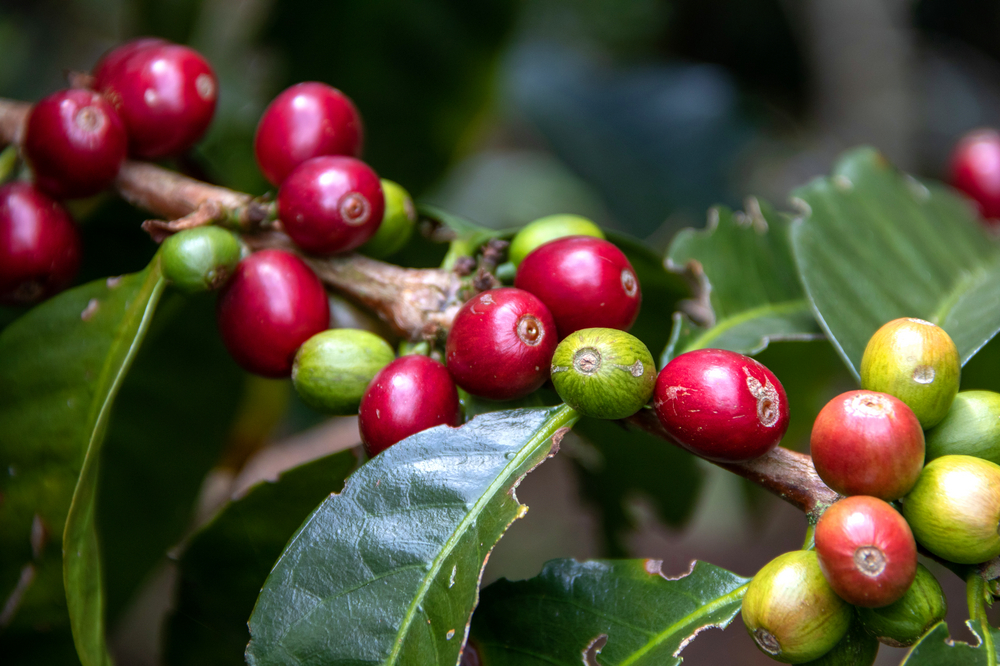
The harvest is not carried out on the finished beans, but on the coffee cherries. The cherry envelops the coffee seeds in several layers and protects them during the ripening process.
There are two common methods of harvesting the cherries: picking and stripping.
Picking: Here, only the ripe cherries are picked by hand, which is time-consuming but guarantees the highest quality.
Stripping: In stripping, on the other hand, all the cherries on a plant are harvested at once – both ripe and unripe fruit. This method is faster as it is carried out by machine. However, it can increase the amount of work required for subsequent sorting.
What is the coffee cherry?
The coffee cherry is what matters when you want to enjoy your favourite coffee. It is the fruit of the coffee plant, inside which the actual coffee beans are found. Each cherry usually contains two seeds, which are processed after harvesting. In some countries, the red, sweet fruit husk is also used for tea or natural cosmetics. The ripeness of the cherry is crucial for the quality of the beans – only deep red fruits make it into the harvest basket.
Regional characteristics: Is coffee grown in Germany or Europe?
We all love regionally produced products. Is it realistic to expect your coffee to come from your neighbour's farm in the near future? Unfortunately not. Coffee cultivation in Germany or Europe is hardly possible due to the prevailing climate. As we have already learned, coffee plants need tropical conditions with consistently high temperatures and humidity. Nevertheless, there are experimental projects, for example in greenhouses or on the Canary Islands, where the climate is somewhat more suitable. These experiments show that European coffee is theoretically possible, but would hardly be economically competitive.
Theoretically, you could also grow a coffee plant at home, but this requires a lot of patience, as it often takes several years before the first harvest. So why not enjoy your coffee stress-free at an event catering with Coffee-Bike and experience real coffee enjoyment without waiting.
Coffee origin – countries around the equator
The home of coffee lies between the northern and southern tropics, i.e. in the region around the equator. And yes, this is due to the climatic conditions. But what is exciting is that each country has its own varieties, traditions and processing methods. You can even taste these in your cup. While Ethiopian coffee is described as particularly fruity and floral, Brazilian varieties are often known for their chocolatey/nutty flavour.
Where are coffee beans grown? – An overview of the most important coffee-growing regions
The most important coffee-growing countries are located in these regions:
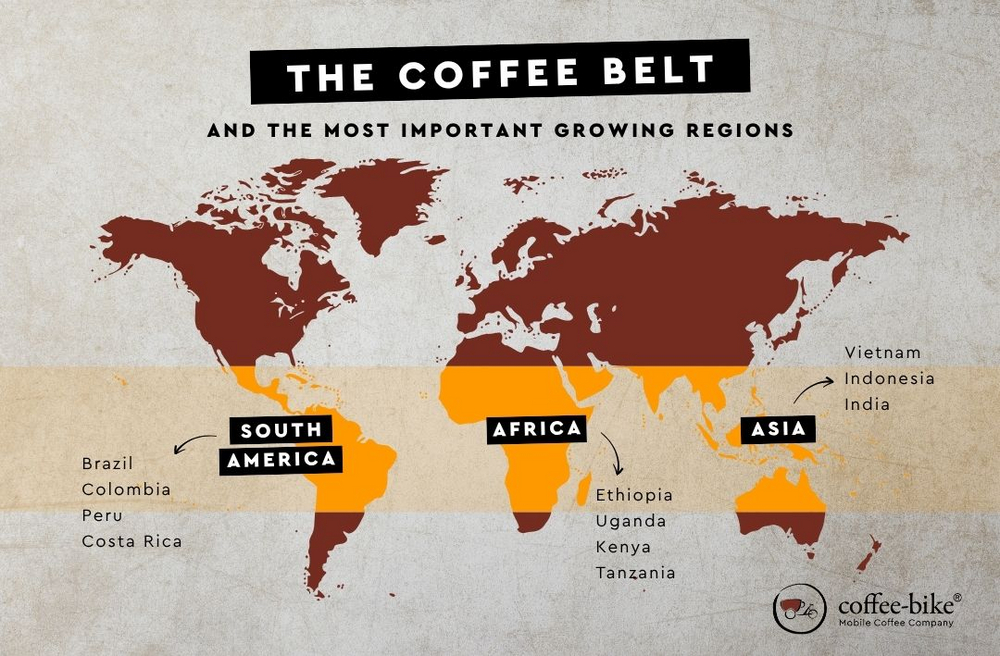
South America: Brazil, Colombia, Peru and Costa Rica.
Asia: Vietnam, Indonesia and India.
Africa: Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya and Tanzania.
These countries offer optimal conditions for coffee cultivation, from fertile soils and the right climate to ideal altitudes. Did you know that Brazil is the absolute leader among coffee producers?
The coffee belt: What is it and which regions does it cover?
The so-called coffee belt refers to the zone around the equator where the climatic conditions are ideal for coffee cultivation. It stretches across South America, Africa, Asia and parts of Oceania. Temperatures between 18 and 25 degrees, abundant rainfall and fertile soils are a given here. These regions are mostly located at altitudes between 600 and 2000 metres.
Origin and Production: How is coffee produced and who is the largest coffee producer in the world?
The production of coffee involves many steps, from cultivation and harvesting to roasting. The three largest coffee producers are Brazil, Vietnam and Colombia, with Brazilian coffee having been the undisputed leader for decades.
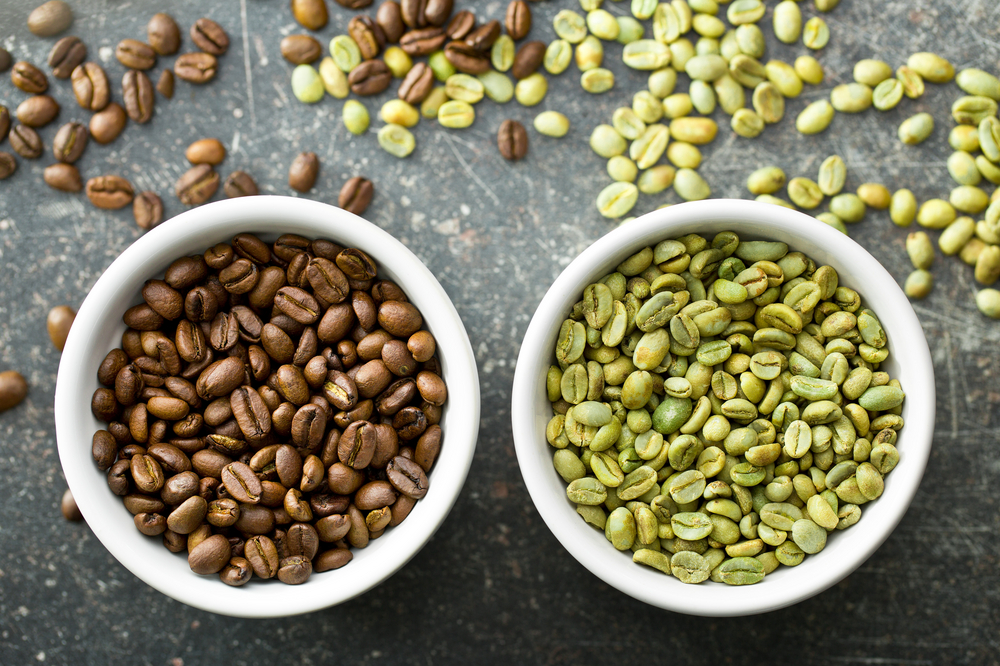
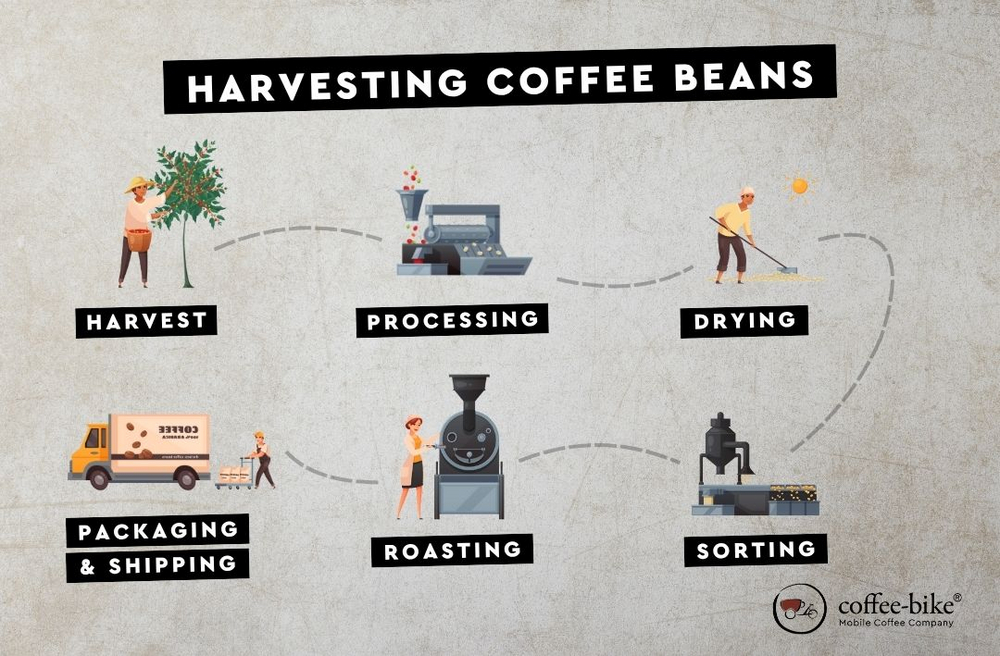
Once the coffee cherries have been harvested, the actual processing of the beans begins. This can be divided into several steps:
Processing (washing or drying):
Wet process (washing): The cherries are peeled, fermented and washed to remove the pulp. This ensures a clear, clean flavour.
Dry process (natural): The cherries are sun-dried before the beans are removed. This method produces strong, full-bodied flavours.
Drying: The beans are further dried until an optimal moisture content of about 10–12% is reached.
Sorting and quality control: The coffee seeds are carefully checked for size, shape, weight and any defects. Only high-quality beans are exported.
Roasting: During this step, the beans develop their characteristic aroma. The temperature, duration and degree of roasting determine the final flavour.
Packaging and shipping: After roasting, the beans are packaged and delivered to wholesalers, coffee bars or our Coffee Bike headquarters, for example.
Discover the Coffee-Bike and see what equipment we use to prepare our beans fresh before your eyes.
Best coffee in the world – high altitudes
The quality of a coffee bean depends heavily on the altitude at which it is grown. At higher altitudes, the plants grow more slowly, resulting in denser bean tissue and a more intense aroma. Such highland coffees are particularly sought after because they develop complex flavours of chocolate, berries or nuts.
Coffee from Indonesia
Indonesian coffee has a long tradition and is characterised by its strong, earthy flavour. Varieties such as Sumatra, Java and Sulawesi are particularly well known. The tropical climate and volcanic soils provide ideal conditions for aromatic beans with low acidity. Many Indonesian coffees are hand-picked in small quantities and sun-dried. This gives them their typical full-bodied character.
Coffee from Guatemala – coffee plants at an altitude of 900 metres
Guatemala is one of the countries with the most diverse coffee profiles in the world. Most plantations are located between 900 and 2,000 metres above sea level, where cool nights and nutrient-rich volcanic soils create perfect conditions. Guatemalan coffee is known for its balanced aroma, fine acidity and notes of cocoa and nuts. Regions such as Antigua and Huehuetenango in particular produce coffee with a great flavour.
Quality criteria: What makes the best coffee plant?
The quality of a coffee plant depends on several factors, including variety, climate, soil conditions and the care provided by the coffee farmer. The bean variety is particularly important, as it lays the foundation for flavour, aroma and cultivation requirements.
Robusta or Arabica? An overview of the two best-known varieties:
• Arabica beans:
o Prefer to grow at higher altitudes and require a temperate, consistent climate.
o They have a finer, more aromatic flavour with a slight acidity and often fruity or floral notes.
o Arabica coffee contains less caffeine, but the beans are more susceptible to disease and pests.
• Robusta beans:
o Robusta is more resistant, grows at lower altitudes and tolerates warmer climates and higher humidity.
o It has a stronger, often more bitter flavour and contains significantly more caffeine.
o Due to its robustness, Robusta is easier to cultivate, but is often considered less refined in terms of taste.
In addition to the variety, care during harvesting plays an important role: only ripe cherries produce beans with a convincing flavour. After that, the processing determines the final aroma.
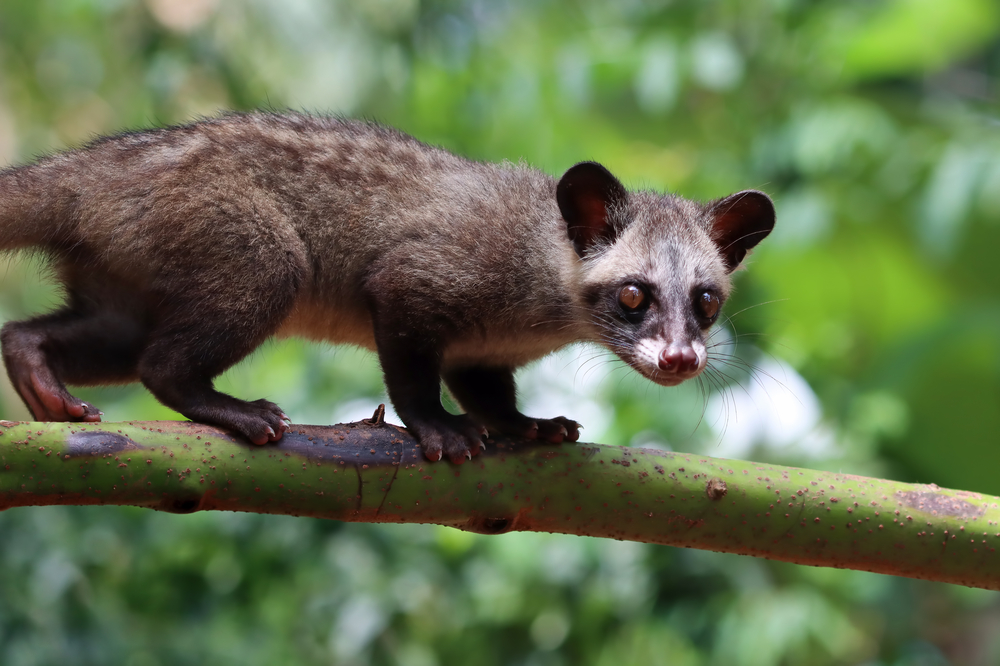
Exotic coffee varieties: What is the name of the coffee made from cat faeces and what distinguishes special varieties?
The famous ‘Kopi Luwak’ comes from Indonesia and is the so-called coffee made from cat faeces. Civet cats eat the coffee cherries, digest the pulp and excrete the beans. Fermentation in the digestive tract produces a particularly mild flavour. However, production is controversial as it is often associated with animal suffering.
Where can you find the best coffee beans in the world?
You have learned that the quality of coffee beans is highest where climate, soil and altitude interact perfectly. Tropical temperatures, regular rainfall and shady growing areas create ideal conditions. In addition, there are of course various factors that play a role in harvesting, such as quality seals and certifications. Probably best known in Europe is the Fair Trade Organic Coffee certification, which is intended to inform end customers about high quality standards and compliance with certain requirements in coffee production.
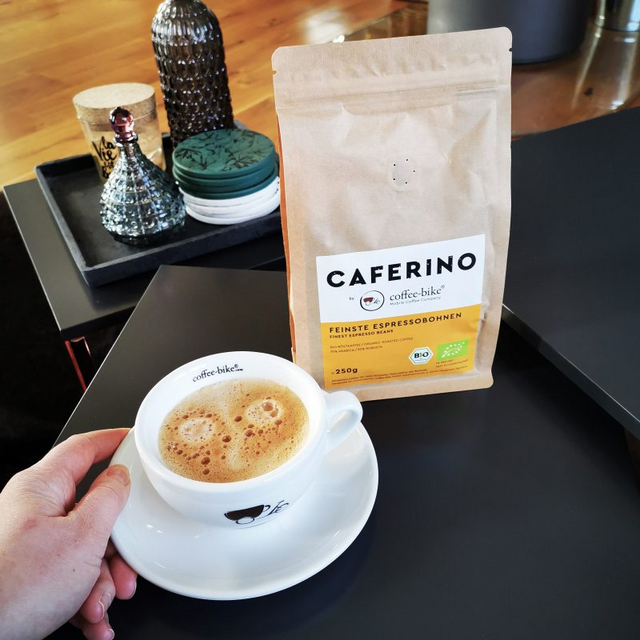
At Coffee-Bike, we attach great importance to quality and origin, which is why our Caferino organic coffee and espresso beans come from carefully selected highland regions of Peru and Central America. These Arabica beans impress with their harmonious, full-bodied aroma, which develops its full depth through traditional long-term roasting. The result is a mild, balanced coffee with a fine acidity and subtle character.
For lovers of stronger roasts, there are Caferino espresso beans, a balanced blend of 70% Arabica and 30% Robusta beans. They captivate with a more intense flavour with subtle notes of nut and chocolate and form a velvety crema – perfect for cappuccino or espresso.
If you want to discover coffee diversity, Coffee-Bike is the right place for you.
How are coffee beans decaffeinated?
Have you ever wondered whether decaffeinated beans are a special variety? No, they are not. To enjoy coffee without caffeine, the green, unroasted bean undergoes a decaffeination process. This involves removing the caffeine using water, solvents or carbon dioxide. However, decaffeinated coffee is never completely caffeine-free and may contain up to 0.1% caffeine (according to EU guidelines). After decaffeination, the coffee is roasted and processed as usual.
Decaffeination processes compared: chemical and natural methods
All decaffeination processes have one thing in common: caffeine is water-soluble, so water always plays a central role. In chemical processes such as the dichloromethane or ethyl acetate method, the coffee beans are first treated with hot steam to swell the cell structure. They are then placed in contact with the solvent for several hours, which dissolves the caffeine from the beans. This is followed by thorough drying, during which the solvent is separated from the beans again.
Natural processes are described in a way that even laypeople can understand, making them seem less like scary laboratory experiments. This is why they are considered particularly gentle.
These processes include the Swiss water process and CO₂ decaffeination. In the latter, the coffee beans are first soaked in water, then pressurised and carbon dioxide is added. The CO₂ extracts the caffeine without affecting the other flavourings.
These gentle methods largely preserve the natural aroma of the beans and are therefore particularly valued for high-quality coffees. Although they are more complex, the result is impressive in terms of purity, quality and full flavour.
Incidentally, you won't find any decaffeinated beans at the Coffee-Bike. As an alternative, we offer other hot drinks such as tea or cocoa. We use the work surface on the Coffee-Bikes as efficiently as possible, so that there is only one grinder and only one type of bean is prepared.
Effects of decaffeination: How does it change the taste of the beans?
Decaffeination can cause subtle changes in taste. Since caffeine itself tastes slightly bitter, decaffeinated coffee often tastes a little milder. However, some processes also remove aromatic oils from the beans, which can lead to a less intense flavour. Modern methods minimise this effect and ensure almost identical results. Today, the difference is usually only noticeable to trained palates.
Is decaffeinated coffee healthier?
Not automatically. Whether decaffeinated coffee is healthier depends, among other things, on the decaffeination method used. However, the advantages can include better sleep and the absence of typical coffee side effects such as nervousness or increased heart rate. Nevertheless, every body reacts differently, so the effect can vary from person to person.
FAQ – Everything you need to know about coffee at a glance
1. Where is coffee grown and where does coffee come from?
Coffee is mainly grown in countries around the equator, including Brazil, Colombia, Vietnam, Indonesia and Ethiopia.
2. How is coffee grown?
The coffee plant needs a tropical climate, fertile soil and often shade. After careful cultivation, the cherries are harvested by hand or machine, then dried, processed and roasted.
3. What are the names of the four coffee-growing regions?
The most important coffee-growing regions worldwide are located in:
• South America – e.g. Brazil, Colombia, Peru, Costa Rica
• Asia – e.g. Vietnam, Indonesia, India
• Africa – e.g. Ethiopia, Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania
• Latin America as a whole – includes many countries in Central and South America
4. Where does the best coffee in the world come from?
Particularly high-quality coffee often comes from highland regions with an ideal climate. Of course, you can get the best coffee at Coffee-Bike.
5. Who is the largest coffee producer in the world?
Brazil is the world's largest coffee producer, supplying around a third of the world's coffee.
6. What is the name of the coffee made from cat faeces?
The famous coffee made from cat faeces is called Kopi Luwak. The cherries are eaten by civet cats and fermented in their digestive tract before the beans are collected.
7. How is coffee decaffeinated?
Coffee can be decaffeinated by extracting the caffeine from the beans. Common methods include the water method, the CO₂ method or the chemical solvent method, whereby the flavours are preserved as much as possible.
8. What is the coffee belt?
The coffee belt is the region around the equator where coffee grows best. It covers parts of South America, Africa and Asia, as the temperature, rainfall and altitude here offer ideal growing conditions.
9. Where can I buy the best coffee?
You can experience the best coffee directly with us – with the Coffee-Bike. Our mobile coffee bars bring freshly roasted and certified organic beans directly to your events, company parties or private functions.
Conclusion – Enjoy the best coffee at your event
The journey from coffee plant to finished cup is fascinating and complex – climate, soil, variety and processing shape every single flavour.
With a Coffee-Bike, we bring this variety directly to your events. Although we do not offer decaffeinated coffee, we do offer many delicious caffeine-free alternatives such as cocoa or iced drinks. This means that all guests can enjoy a special treat, regardless of whether they want to drink caffeine or not. With certified organic beans, the best coffee drinks, careful preparation and authentic barista craftsmanship, every Coffee-Bike coffee catering service at your event will be an unforgettable experience. Rent your Coffee Bike!
These articles might intrest you: